Arthritis
A BRIEF LOOK AT ARTHRITIS
What is Arthritis?
Arthritis is a painful joint condition caused by inflammation. Joints are where two bones connect; this connection facilitates movement. There are many variations of arthritis; over a hundred types have been identified.
Three common types of arthritis are: –
- Osteoarthritis, also called degenerative joint disease, is the wear and tear of the cartilage in the joints. This is one of the most common types of arthritis, especially among the elderly.
- Rheumatoid arthritis, also popular among the elderly, occurs when the body’s immune system attacks its healthy joint tissues. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease. Autoimmune diseases are mal health conditions in which the body’s immune system attacks itself.
- Gout arthritis is a deposition and buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints. This condition is more prominent in the big toe; however, it can affect other body areas.
Symptoms of Arthritis
The various types of arthritis may have distinctive patterns in how they manifest in an individual. The presence of pain (periodic, constant, or flare-ups), swelling, stiffness, loss of range of motion, heat, and redness in the joints are some common indicators of the presence of arthritis.
Some Causes and Risk Factors
The above shows that the wear and tear of the cartilage causes osteoarthritis. A malfunctioning immune system causes rheumatoid arthritis, and too much uric acid forms crystals in the joints, resulting in gout. Other causes of arthritis are: –
- The genes (inherited)
- Injury
- Infections such as Lyme disease
- Lack of exercise
- Wrong eating habits (lead to metabolic disorder)
Who is most at risk of getting arthritis?
- Senior Age: Reduced vigor, slowed metabolism, wear and tear are some of the conditions that come with aging, which creates a strong probability for arthritis.
- Gender: Most forms of arthritis are more prominent in females.
- Genetics: Studies have found that some gene traits are more probable to cause specific types of arthritis.
- Occupation: Jobs that require repetitive joint movements, such as twisting the wrist or bending the knee, can lead to osteoarthritis.
- Overweight: Excess body fat can contribute to the degeneration of the joints.
Note, certain risk factors lead to specific forms of arthritis.
How is arthritis diagnosed?
Arthritis is diagnosed using imaging techniques, such as x-rays, CT scans, MRI, and ultrasound.
Treatment
The treatment for arthritis, depending on the severity, includes: –
- Prescription or non-prescription pain-relieving and inflammation medication
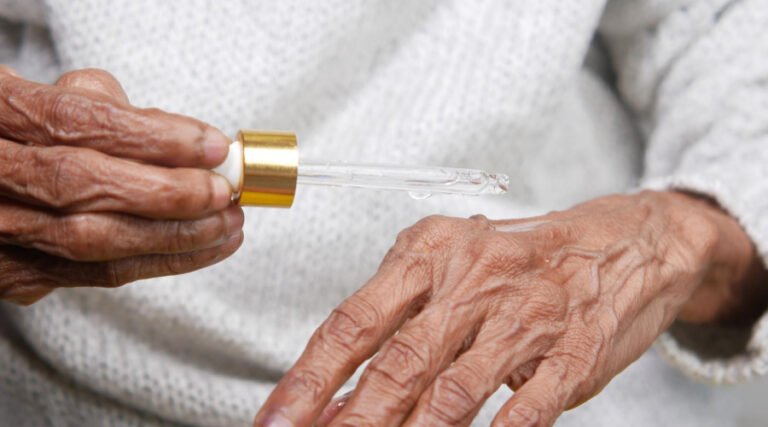
- Topical pain-relieving ointments, creams, or gels
- Braces or splint (for joint support)
- Injections or infusions
- Physical therapy
- Surgery: Joint replacement (arthroplasty) or joint fusion
Tips for Managing Arthritis at Home
To alleviate arthritis pain/inflammation and improve joint functions, these home remedies may help: –
- Moderate exercise: Keep the affected joints active but in moderation. Do not overdo the exercises. Too much exercise can be as harmful as doing none. Exercise improves joint health.
- Hot or cold treatment: Put an ice pack or heat pack on a thin rag and put it on the affected area. This can relieve the pain. The rag protects the skin from getting burnt.
- Take anti-inflammatory supplements such as vegan glucosamine, chondroitin, and omega-3 fats.
- Turmeric spice also has anti-inflammatory properties. Mix about a half teaspoon of the turmeric spice in a cup of lukewarm water; sip on this. There are also turmeric supplements. Always use natural (plant-based) sources of turmeric.
- Lifestyle changes such as: –
- Losing weight (where this is applicable)
- Drink an adequate quantity of water: Water gently detoxes the body and can “help” to gradually reverse certain medical conditions.
- Eliminate sweet foods such as pastry, ice cream, and chocolate.
- Try going on a plant-based diet. This lifestyle choice has proven beneficial in reversing or reducing many disease conditions.
- Have a regular exercise regime, such as walking, swimming, or gardening.
- Exercise encourages good blood circulation, strengthens joints and keeps them flexible.
- Exercise improves mood.
- Avoid smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages.
- Alleviate stress.
Source
- Mayo Clinic Staff. (2023). Arthritis. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/arthritis/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20350777
- MedlinePlus. (2023). Arthritis. https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/001243.htm
- NIH. (2022). Arthritis. https://www.niams.nih.gov/health-topics/arthritis
- NIH. (2023). Osteoarthritis. https://www.niams.nih.gov/health-topics/osteoarthritis
- Rath, L. (2022). What is Arthritis? https://www.arthritis.org/health-wellness/about-arthritis/understanding-arthritis/what-is-arthritis

